
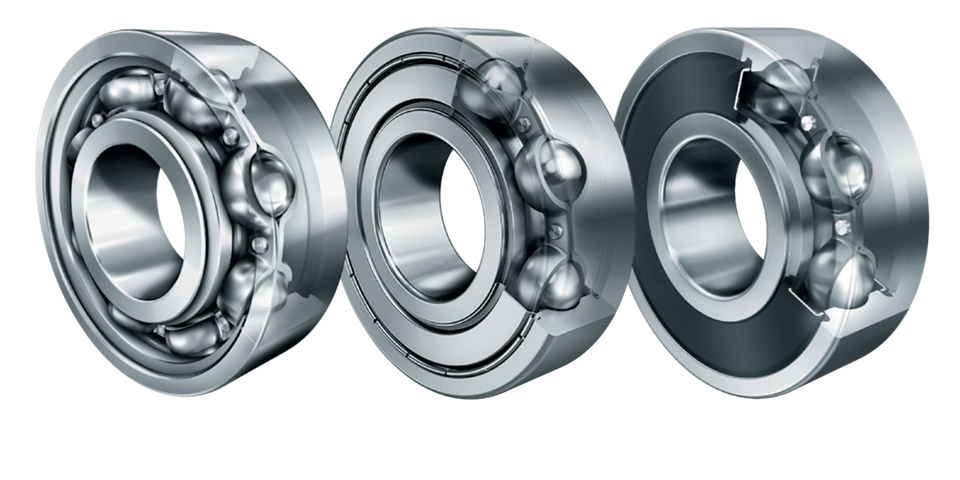
Bearings World is a trusted name when it comes to Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE, supplying industries, automotive applications, and engineering companies across Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah, Ajman, Ras Al Khaimah, Fujairah, and Umm Al Quwain. Known for durability, precision, and high performance, our range of Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE is designed to handle radial and axial loads with efficiency.
Whether you need Deep Groove Ball Bearings Dubai, Deep Groove Ball Bearings Abu Dhabi, or Deep Groove Ball Bearings Sharjah, Bearings World ensures reliable supply, competitive pricing, and premium quality.
What Are Deep Groove Ball Bearings?
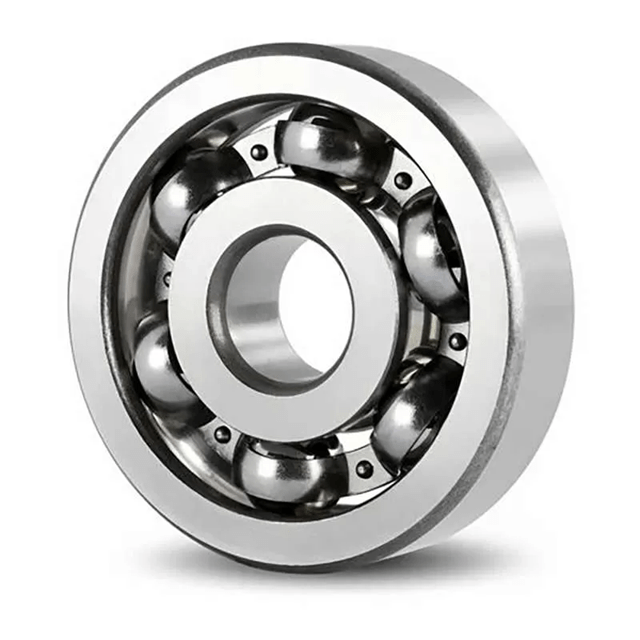

Deep groove ball bearings are the most widely used type of rolling bearings in the world. They are versatile, reliable, and capable of handling both radial and axial loads. Bearings World supplies Single Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE, Double Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE, and advanced types like High Precision Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE for industries that demand accuracy and long service life.
Types of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
As a premium Deep Groove Ball Bearings Supplier UAE, Bearings World offers:
Single Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Compact design for high-speed applications.
Double Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Greater load-carrying capacity.
Stainless Steel Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Excellent resistance to corrosion.
Sealed Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Maintenance-free, ideal for dusty or wet conditions.
Open Type Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – For applications where sealing is not required.
Miniature Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Perfect for small devices and precision instruments.
Large Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE – Heavy-duty applications in industries and power plants.
Design Variations, Materials, and Manufacturing Process
The versatility of rolling element bearings arises not only from their performance but also from the diversity of designs available. Engineers can select from a wide range of configurations, each offering unique strengths tailored to specific applications.
Common Design Variations
Single-Row Design
This is the most widely used type, featuring a single row of rolling elements. It is compact, cost-effective, and capable of handling moderate radial and axial loads.Double-Row Design
Incorporating two rows of rolling elements, this design offers higher load capacity and greater rigidity. It is particularly useful in applications where alignment is critical or when loads are heavier.Sealed Units
These designs come with integrated seals that protect the internal components from dust, moisture, and other contaminants. They are often pre-lubricated, reducing maintenance needs.Shielded Variants
Unlike sealed units, shielded types use metal covers to protect against larger debris while still allowing limited relubrication if needed.Angular Contact Versions
These are optimized for applications requiring high precision and the ability to carry combined loads, especially axial loads in one direction.Thin Section Models
Designed for environments where space and weight are critical, such as robotics or aerospace, thin-section variants offer compactness without sacrificing performance.High-Speed Configurations
Specially engineered for applications with extremely high rotational speeds, these models minimize friction and heat buildup, ensuring reliable operation.
Materials Used
The choice of materials plays a significant role in determining durability, resistance, and performance.
High-Carbon Chrome Steel: The most common material, offering a balance of strength, wear resistance, and affordability.
Stainless Steel: Provides resistance to corrosion and is widely used in food processing, medical equipment, and environments exposed to moisture.
Ceramic Hybrids: Combining steel rings with ceramic rolling elements, these are ideal for high-speed and high-temperature applications due to reduced friction and greater heat resistance.
Polymers and Composites: Used in specific industries where lightweight, noise reduction, or chemical resistance is more critical than heavy load capacity.
Heat Treatments
To enhance durability, steel components often undergo heat treatments such as carburizing, quenching, and tempering. These processes improve hardness, fatigue resistance, and overall longevity.
Manufacturing Process
Raw Material Selection
High-quality steel bars or tubes are selected and tested to ensure consistency.Forming the Rings
The steel is cut, forged, and machined into inner and outer rings. Precision machining is crucial to ensure tight tolerances.Rolling Element Production
Balls or rollers are manufactured through forging and grinding processes, ensuring perfect roundness and uniform size.Heat Treatment
Both rings and rolling elements are heat-treated to enhance strength and wear resistance.Grinding and Superfinishing
The raceways and rolling elements undergo multiple grinding operations followed by polishing for smooth surfaces. This minimizes friction and noise.Assembly
Rolling elements, cages, and rings are carefully assembled under controlled conditions to prevent contamination.Lubrication and Sealing
Depending on design, grease or oil is added, and seals or shields are installed.Inspection and Quality Control
Each unit undergoes rigorous inspection using advanced measurement tools to verify dimensions, surface finish, and performance.
Advances in Manufacturing
Modern technology has significantly improved efficiency and performance in production. Automation, robotics, and computer-controlled grinding machines ensure accuracy, while non-destructive testing methods detect hidden flaws. 3D modeling and simulation tools also help engineers predict performance under different conditions, leading to better customization.
Coatings and Treatments
To further enhance performance, manufacturers apply specialized coatings:
Phosphate Coating: Adds corrosion resistance.
Teflon Coating: Reduces friction and improves sliding performance.
Black Oxide Treatment: Increases resistance to wear and moisture.
Advanced Ceramic Coatings: Provide extra protection in extreme environments.
Applications Across the UAE
Bearings World provides Automotive Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE, Industrial Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE, and Custom Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE to meet diverse needs. These bearings are widely used in:
Automobiles and motorcycles
Conveyor systems
Electrical motors and pumps
Industrial machinery
Household appliances
Heavy equipment in construction and oilfields
Whether it’s Deep Groove Ball Bearings Fujairah, Deep Groove Ball Bearings Ras Al Khaimah, or Deep Groove Ball Bearings Umm Al Quwain, we ensure coverage across all Emirates.
Why Choose Bearings World?
As a specialized Deep Groove Ball Bearings Supplier UAE, we guarantee:
✅ High-quality OEM and aftermarket products
✅ Wide stock availability for immediate supply
✅ Wholesale and retail options
✅ Precision engineering for long-lasting durability
✅ Distribution across all UAE Emirates
With Bearings World, customers get reliable Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
Distribution Network
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Dubai
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Abu Dhabi
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Sharjah
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Ajman
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Ras Al Khaimah
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Fujairah
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Umm Al Quwain
No matter your location, Bearings World ensures fast delivery of Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE for all industries.
Reliable Performance and Applications
The role of these components in machinery is critical. Their precision and durability help ensure smooth operation across a wide range of mechanical systems. By minimizing friction, they extend the lifespan of equipment and reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Ensures stability in rotating systems
Reduces heat build-up and energy loss
Supports both light-duty and heavy-duty operations
Enhances efficiency in high-speed applications
Material Choices and Benefits
Different materials are selected depending on the operating conditions and specific industry requirements. Choosing the right material improves resistance to wear, corrosion, and extreme temperatures.
Stainless steel: Ideal for corrosion resistance in challenging environments
Alloy steel: Provides strength and durability for demanding use
Specialized polymers: Reduce friction and weight for specific applications
Engineering Design and Variations
The design flexibility allows them to be adapted for countless applications. Options with shields or seals provide additional protection, while open types are well suited for clean and controlled environments.
Sealed designs help block dust, moisture, and contaminants
Shielded types provide long service life with reduced maintenance
Open versions allow easy inspection and lubrication
Industrial and Automotive Uses
These components are widely utilized in sectors ranging from automotive to heavy engineering. Their ability to perform under diverse loads makes them indispensable in many fields.
Automotive systems such as gearboxes, engines, and wheels
Conveyor systems and production machinery
Household appliances requiring quiet and smooth operation
Power tools and compact equipment with high rotational speed
Advantages for End Users
Users benefit from consistent performance, cost savings, and reduced maintenance downtime. By relying on high-quality components, industries achieve better results in both efficiency and safety.
Lower operational costs through reduced wear
Extended service intervals for machinery
Improved reliability across various applications
Where can I buy reliable Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE for industrial and automotive applications?
You can source high-quality Deep Groove Ball Bearings UAE from Bearings World, a trusted supplier across Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah, Ajman, Ras Al Khaimah, Fujairah, and Umm Al Quwain. We provide single-row, double-row, stainless steel, sealed, and custom solutions suitable for automotive, industrial, and heavy-duty applications. With wide stock availability and professional support, Bearings World ensures reliable performance and fast delivery across all Emirates.


Bearings World Auto spare parts Trading LLC, Sharjah br. hold pride in introducing ourselves as the part of Bearings world group which is one of the leading source for all types of bearings in U.A.E market.
Copyright © 2025 Bearings World. All Rights Reserved. Powered by Adsonz
